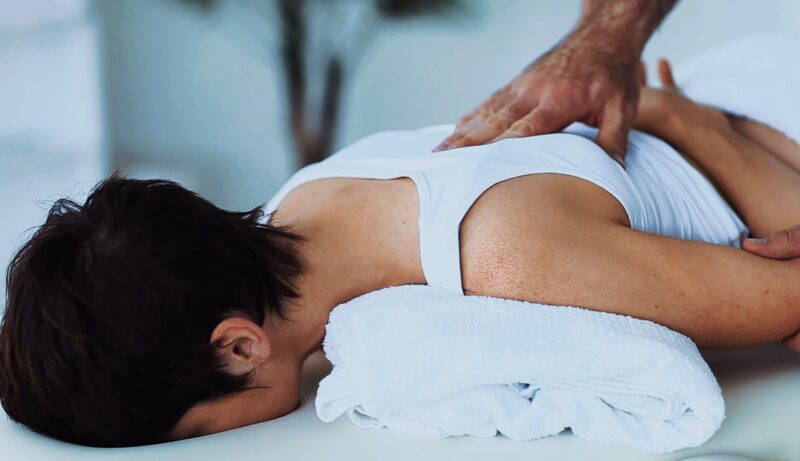
Today I wanted to chat about something super important that affects a lot of people – back pain. Our backs take such a beating every day with work, exercise, sitting for long periods – it’s no wonder so many struggle with discomfort or issues. And it can really put a damper on being active.
Luckily there are options to help beyond just pain meds. Physiotherapy, or “PT” for short, gets to the root of what’s causing issues instead of just masking symptoms. Things like exercises, stretches, and hands-on treatments over time can really make a difference.
Initial assessments
Posture analysis
Spotting and correcting the ways you stand or sit that may stress your back is crucial. By adjusting these habits, you can stop back pain from getting worse and prevent other health issues. Typically, this process involves watching how you move and how you hold yourself when you’re still. To analyze your spine effectively, it’s essential to understand different posture types and potential issues comprehensively
Flexibility tests
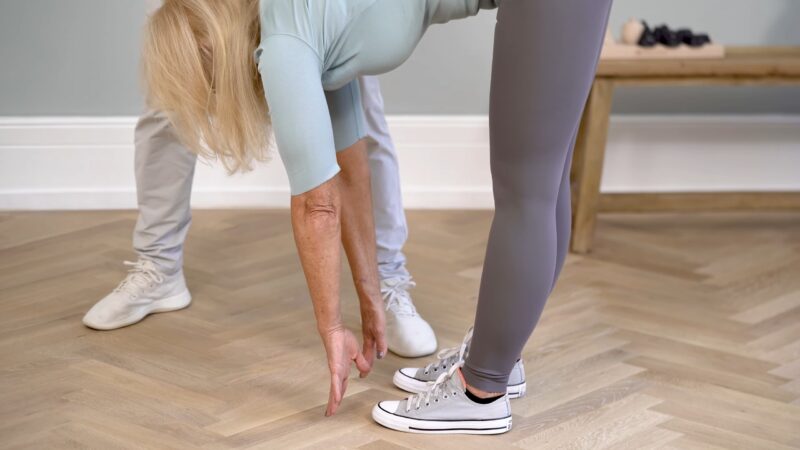

Checking how well you can move can reveal stiffness that might be causing discomfort. If you’re not very flexible, it can make back problems worse and make it harder to move around. By regularly testing how flexible you are, you can see how you’re improving and make changes to your treatment if needed.
Strength evaluations
Determining muscle weaknesses around the spine is critical for developing targeted strengthening programs. Strengthening these muscles can significantly enhance spinal stability and reduce the likelihood of future injuries. This evaluation often includes testing both the core and lower back muscles.
Mobility checks
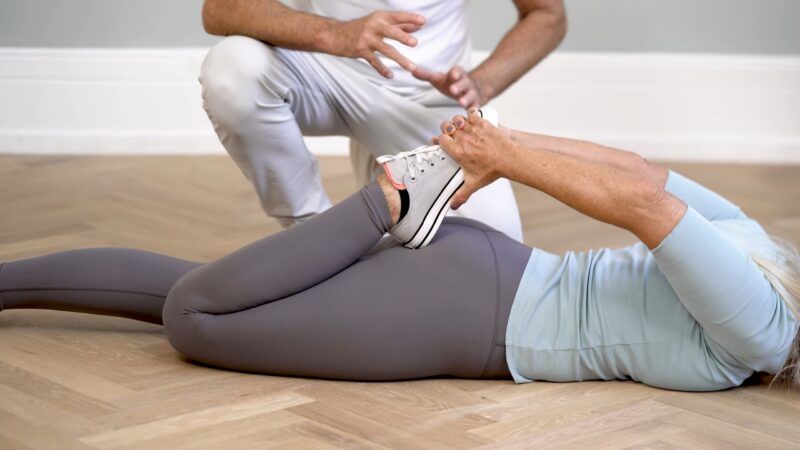

Mobility checks help in tailoring interventions that focus on specific areas of restriction. These assessments guide the development of personalized treatment plans. Improved joint mobility can lead to better alignment and decreased pain.
Core techniques in physiotherapy
1. Manual therapy
-
Massage
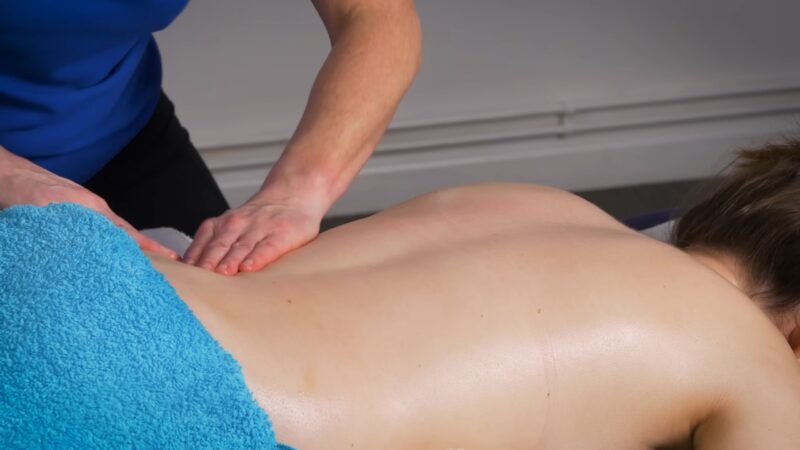
Eases muscle tension and enhances blood flow. Massage therapy helps in relaxing tight muscles and can provide immediate relief from pain. It also reduces stress levels, which can contribute to muscular tension.
-
Mobilization
Increases joint mobility through controlled movements. This technique helps in loosening up stiff joints, particularly in the spinal column, which can improve overall mobility and comfort. Mobilization is often used to restore normal movement to vertebrae that have become misaligned or restricted in their motion.
-
Manipulation
Reduces pain and restores function through precise, forceful adjustments. Manipulation techniques are used to reposition bones and joints, potentially relieving pressure on nerves and correcting alignment issues. It is typically performed by a physiotherapist with specialized training in manipulative therapy.
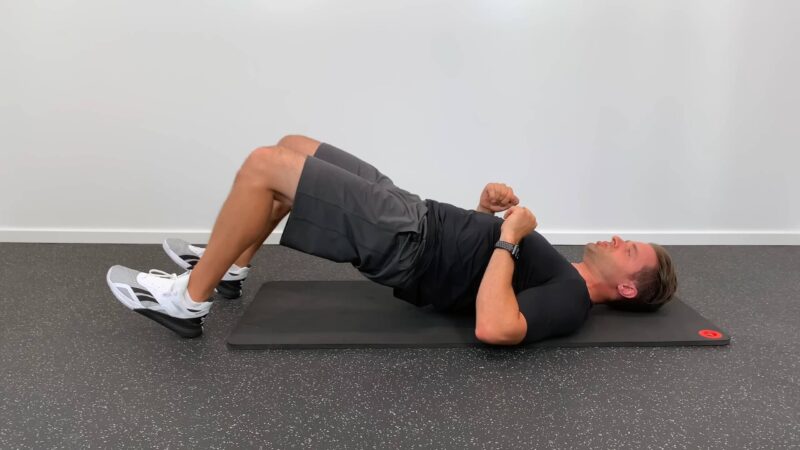
2. Exercise therapy

-
Strengthening exercises
These exercises are designed to build up the muscles that help maintain proper posture and spinal alignment. Stronger back and core muscles can significantly reduce the burden on the spinal column and prevent pain.
-
Flexibility routines
Increased flexibility can alleviate stress on the back by allowing for smoother, more fluid movements. Regular flexibility training can also help prevent injuries that might occur from day-to-day activities.
3. Supportive modalities
-
Heat therapy
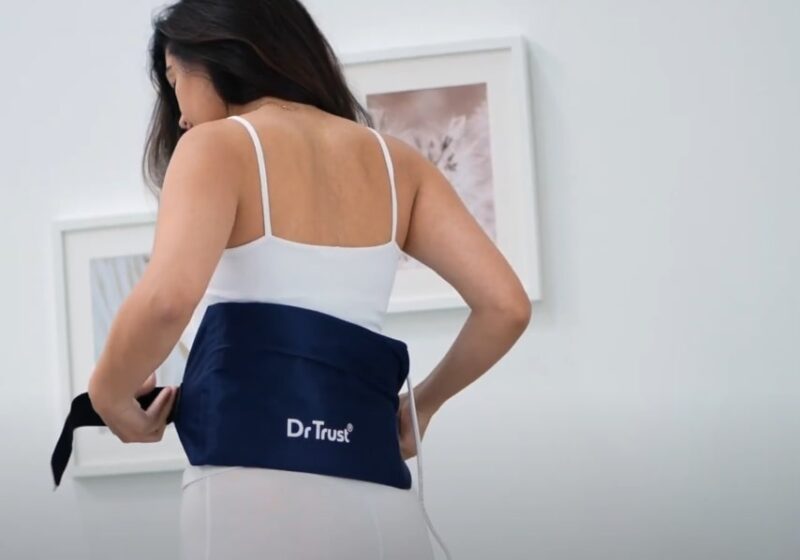

Relieves muscle pain and spasms. Applying heat can increase blood flow to the affected area, which aids in healing and provides a soothing effect. Heat therapy is often recommended for chronic back stiffness and soreness.
-
Cryotherapy
Reduces inflammation and numbs sharp pain. Cooling the affected area helps to decrease swelling and inflammation, offering relief from acute pain. Cryotherapy can be particularly effective immediately after an injury.
-
Ultrasound
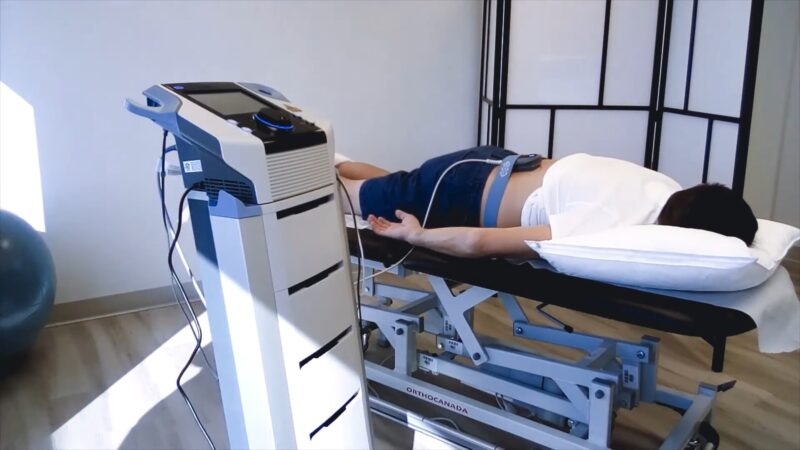
Promotes tissue healing at the microscopic level. Ultrasound therapy uses sound waves to penetrate deep into tissue, promoting cellular repair and increasing circulation. This modality is often used for soft tissue injuries in the back.
-
Electrical stimulation
This technique stimulates muscles through mild electrical pulses, which can help to strengthen them and reduce pain perception. Electrical stimulation is beneficial for patients who might be unable to perform physical exercises.
Preventative strategies and lifestyle advice
Physiotherapy also focuses on prevention, educating patients on how to avoid future back issues through lifestyle and environmental adjustments.
Ergonomic optimization
Setting up your work and living areas to support your spine is really important. By using proper ergonomics, you can greatly lower your chances of getting back pain. This means doing simple things like adjusting your chair height to the right level, organizing your desk properly, or choosing the right mattress and pillows for your bed.
These small changes help keep your body in a more natural and comfortable position as you go about your day.
Regular physical activity
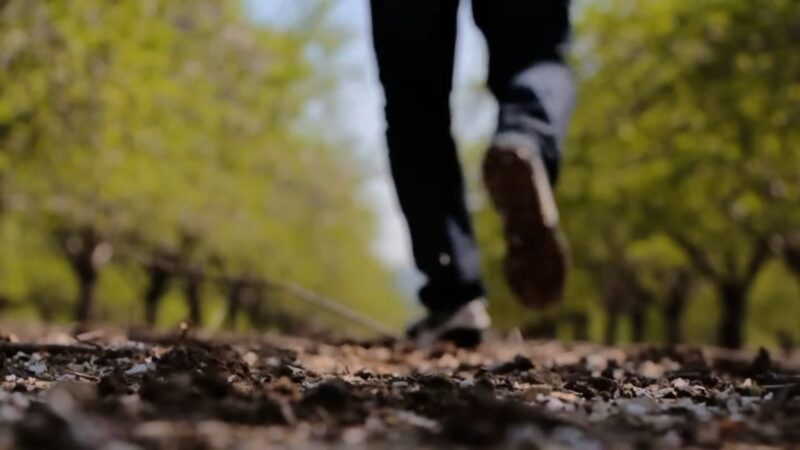

Activities like swimming, walking, or cycling promote overall health without putting undue stress on the back. Sticking with these activities regularly can help keep back pain at bay and build your body’s strength and endurance.
Applying safe lifting techniques
Using your legs instead of your back when lifting heavy objects is crucial for preventing injuries. Learning the right way to lift can help you avoid unexpected strains or sprains. It’s especially important for people whose jobs require lifting heavy items to know and practice these techniques.
The bottom line
Physiotherapy is really amazing at not just treating issues, but preventing them too. Through PT, you gain a strong support system for keeping your back in top shape. Especially if you’re starting a new workout routine, making sure your back is ready is key.
That’s where physiotherapy comes in huge. The pros can strengthen your muscles to handle the activity and new movements safely.

