Numbness and tingling, those weird “pins and needles” feelings, can pop up anywhere on your body. Usually, it’s no big deal—like when your foot falls asleep after sitting weird.
But if it keeps happening, it could be a sign of something more serious, like nerve damage or health issues like diabetes or multiple sclerosis. Knowing what causes these feelings, the symptoms, and how to treat them can help you manage them better.
Key Takeaways
- Numbness and tingling can be caused by various factors, including nerve compression, circulation problems, or specific medical conditions.
- Determining the underlying cause is crucial for appropriate diagnosis and treatment options.
- Early diagnosis and treatment are key to effective management.
Causes
There are several factors that can lead to numbness and tingling. Understanding these can help pinpoint the reason behind your symptoms:
1. Neurological Conditions
Some neurological conditions can cause numbness and tingling. For instance, peripheral neuropathy occurs when peripheral nerves are damaged, often leading to weakness, numbness, and pain in the hands and feet.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is another condition where they are common early symptoms.
2. Circulatory Issues
Poor circulation can also lead to numbness and tingling, as it reduces the blood flow to certain parts of your body. Sitting with your legs crossed or falling asleep on your arm are everyday examples of paresthesia due to temporary circulatory issues.
3. Injuries and Trauma
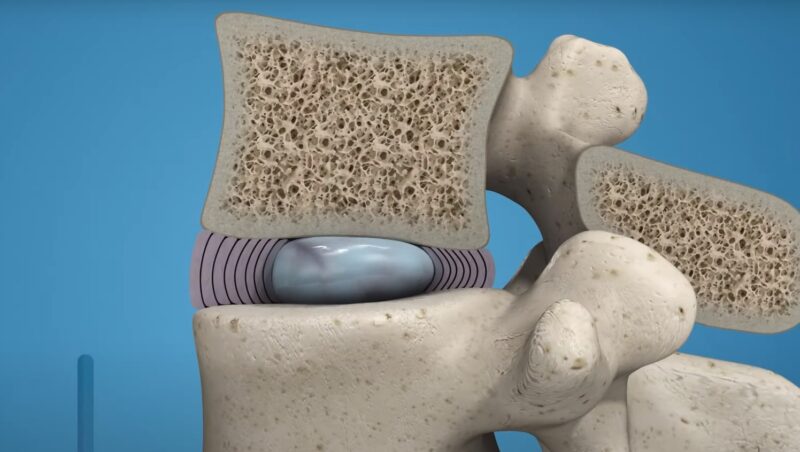
In some cases, numbness and tingling might be the result of injuries and trauma. Peripheral nerve injuries can cause these sensations, as well as herniated discs and spinal cord injuries.
4. Infections and Inflammatory Diseases
Certain infections and inflammatory diseases can also lead to numbness and tingling. For instance, Guillain-Barre syndrome is a disorder in which your immune system attacks your nerves, causing weakness, tingling, and numbness.
While this section outlines some common causes of these symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan tailored to your specific situation.
Symptoms
When it comes to numbness and tingling, several symptoms can clue you in on what’s going on. Here’s what to watch out for:
Chronic Pain

Chronic pain is often accompanied by numbness and tingling. The sensation may manifest as sharp, jabbing, throbbing, or burning pain, which can make it difficult for you to carry out your daily activities.
The Mayo Clinic highlights peripheral neuropathy as a condition that can cause these symptoms. Make sure to consult a healthcare professional if you experience persistent chronic pain.
Muscle Weakness

When experiencing numbness and tingling, you may also notice muscle weakness in the affected areas. This can occur in your hands, feet, legs, and arms.
A common cause of muscle weakness associated with numbness and tingling is multiple sclerosis (MS), a condition where the body’s immune system attacks the central nervous system. It is essential to seek medical advice if muscle weakness begins to affect your ability to perform daily tasks.
Loss of Coordination
Loss of coordination can also occur in conjunction with numbness and tingling. This might lead to:
- Difficulty in maintaining balance
- Inability to perform simple motor tasks
- Increased risk of falls or injuries
Conditions such as peripheral neuropathy and MS may contribute to loss of coordination. If you notice a decline in your coordination, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper assessment and diagnosis.
In summary, numbness and tingling can be accompanied by chronic pain, muscle weakness, and loss of coordination. Always consult a healthcare professional if you experience these symptoms to receive proper diagnosis and treatment, ensuring that your health is well-maintained.
Diagnosis
To determine what’s causing your numbness and tingling, your doctor might use several approaches:

Physical Examination
During a physical examination, your doctor will closely observe your body for any signs of injury or inflammation that may cause numbness and tingling. They may also gently touch various parts of your body to check for any areas of tenderness or numbness.
Mayo Clinic recommends seeking medical advice if you experience intermittent numbness or tingling in one or both hands.
Neurological Diagnostic Tests
Neurological diagnostic tests are essential to determine the exact cause of your numbness and tingling. Some of the tests your doctor might perform or recommend include:
- Nerve conduction study: This test measures the speed at which electrical signals travel through your nerves. Slower signal transmission may indicate peripheral neuropathy.
- Electromyography (EMG): During an EMG, a small needle-like electrode is inserted into a muscle to measure electrical activity. This helps determine if they are due to muscle or nerve issues.
These tests will provide valuable information to your healthcare provider about the underlying cause of your symptoms. Peripheral neuropathy is a common issue diagnosed using these tests.
Blood Tests
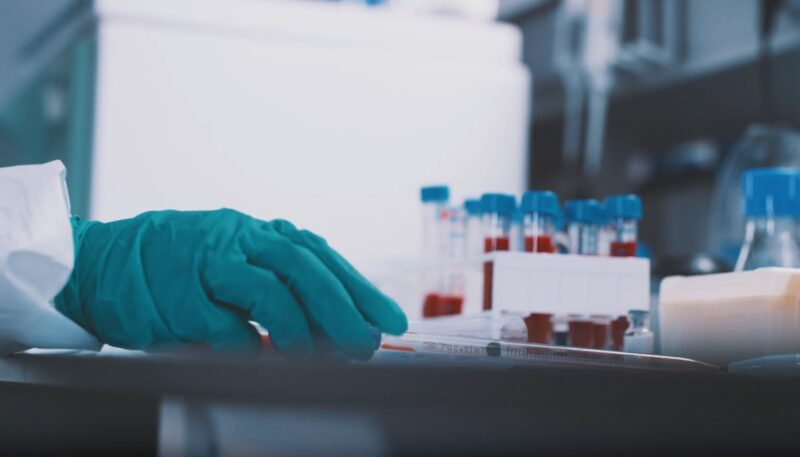
Finally, blood tests can also be beneficial in diagnosing the cause of numbness and tingling. They can help identify any underlying issues such as vitamin deficiencies, diabetes, or kidney problems, which may be contributing to your symptoms.
As part of comprehensive diagnostic efforts, Cleveland Clinic suggests conducting blood tests to rule out other causes of paresthesia.
How to Treat Numbness and Tingling?
There are different ways to treat numbness and tingling, depending on the cause. Here are some common treatments:
Medications
There are a variety of medications that can be used to help manage numbness and tingling. Some common options include:
- Antidepressants: Certain antidepressants, such as duloxetine and nortriptyline, have been found effective in treating neuropathy.
- Anticonvulsants: Medications like pregabalin, originally developed to treat epilepsy, can also be used to manage symptoms.
- Pain relievers: Over-the-counter pain medications, such as ibuprofen, and prescription pain relievers may help alleviate discomfort.
It’s important to consult with your doctor to determine the best medication for your specific situation.
Therapies and Rehabilitation

In addition to medications, various therapies and rehabilitation techniques can help manage this problem:
- Physical therapy: Working with a physical therapist, you can learn exercises to improve your muscle strength, flexibility, and overall function.
- Occupational therapy: This type of therapy focuses on helping you perform normal daily activities with less discomfort.
- Massage therapy: Gentle massage can help improve circulation and alleviate muscle tension that may be contributing to numbness and tingling sensations.
Your healthcare provider can guide you in choosing the most suitable therapy for your needs.
Surgical Interventions
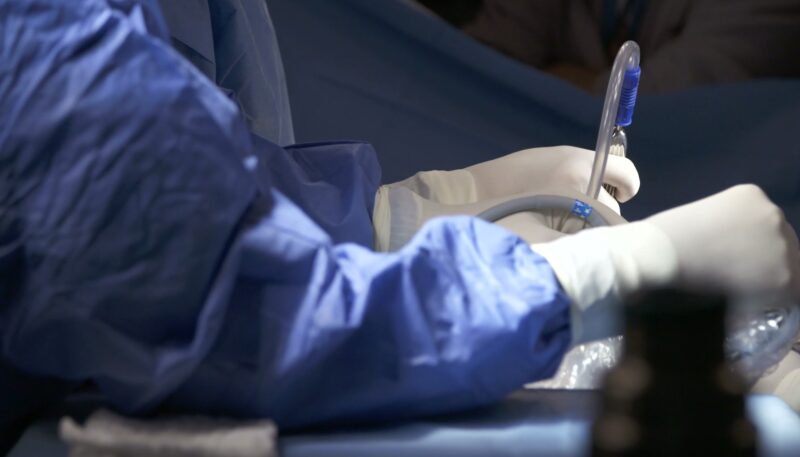
In some cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to address the underlying cause of numbness and tingling:
- Carpal tunnel release: This procedure involves cutting the ligament that’s compressing the nerves in the wrist, relieving carpal tunnel syndrome symptoms.
- Discectomy: If a herniated disc in the spine is causing pressure on a nerve, surgery may be needed to remove the damaged disc, decreasing sensations of these symptoms.
Surgical options should be thoroughly discussed with your healthcare provider to determine the risks and benefits, as well as other available alternatives.
Prevention of Numbness and Tingling
Keeping numbness and tingling at bay involves a mix of lifestyle changes and practical adjustments:
Lifestyle Changes

To prevent and manage numbness and tingling, it’s essential to adopt some healthy lifestyle habits. Maintain a well-balanced diet that includes sufficient vitamins and minerals. Ensure you’re consuming enough B vitamins, such as B6, B12, and folate, which play a crucial role in nerve health.
Stay physically active to support your circulatory system and reduce the risk of diabetes-related neuropathy. Additionally, limit alcohol intake, avoid smoking, and manage stress, as these factors can contribute to nerve damage.
Ergonomic Adjustments
Using proper ergonomics at work and home can help alleviate and prevent numbness and tingling. Adjust your workspace to ensure you’re using an ergonomic chair, desk, and accessories like wrist supports.
Maintain correct posture while working, and take regular breaks to stretch and change positions. When performing tasks that involve repetitive movements, such as typing or using tools, make sure your wrists, fingers, and other body parts are well-supported and positioned correctly.
| Ergonomic Adjustment | Example |
|---|---|
| Chair | Adjust seat height and backrest angle for proper lumbar support. |
| Desk | Ensure the desk height accommodates your elbows being at a 90-degree angle. |
| Keyboard | Use a keyboard with a slight slope or ergonomic design. |
| Mouse | Choose a mouse that fits your hand size and grip preference. |
Regular Health Checks
Staying updated on your health is crucial for preventing and managing numbness and tingling. Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor your overall health and to identify any potential concerns early.
For individuals with diabetes, maintain control of blood sugar levels and frequently check your feet for any signs of numbness, tingling, or injury.
In summary, lifestyle changes, ergonomic adjustments, and regular health checks are key aspects in the prevention and management of numbness and tingling. Adopting these measures can improve your overall well-being and reduce the risk of nerve-related issues.
FAQ
Conclusion
While numbness and tingling are often no big deal, they can be signs of more serious problems if they happen a lot. Understanding what causes them and knowing the treatment options are key to handling these sensations.
Always talk to a doctor if you’re worried about numbness or tingling so you can get the right help.

