Did you know improving posture for health can have a big impact on how you feel each day? The way you hold yourself can affect your muscles, bones, and even your mood. It’s important to be aware of your posture so you can feel your best.
There are various types of posture, some of which can lead to problems if not addressed properly. Good posture is essential for reducing the risk of developing musculoskeletal issues and maintaining an active lifestyle.
In this article, we’ll explain what good posture is, some common posture problems, and the easy things you can do to feel stronger and more confident.
Key Takeaway
- Improving posture for health is vital for reducing musculoskeletal issues and enhancing overall health and well-being
- Various postures, including neutral, forward head, kyphosis, flat back, and swayback, have specific impacts on health.
- Maintaining the natural curves of the spine is fundamental for good posture, helping to distribute weight evenly.
- Proper ergonomics, regular exercise, and stretching, along with the use of posture training tools, are key strategies for improving posture.
- Beyond musculoskeletal benefits, good posture supports respiratory and digestive health.
Fundamentals
Maintaining proper posture is crucial to support the skeletal system and spinal stability. It also allows for more efficient muscle function and can minimize the risk of various pains and injuries.
There are a few key components necessary for good posture, and recognizing them can lead to improved overall health and well-being. One of the most important aspects of good posture is the alignment of the spine.
The spine consists of various natural curves, such as the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar curves. Proper posture should maintain these curves and avoid placing additional strain on any of them. A neutral spine signifies a correct posture, wherein the head, neck, and shoulders are positioned directly above the hips.
Another essential feature of proper posture is the balance of weight distribution in the body. This includes equal weight-bearing on both feet and the ability to maintain equilibrium during dynamic movements. Posture is not only important while standing but also while sitting, walking, and carrying out various exercises.
Posture problems can stem from different factors, such as weak or tight muscles, poor movement habits, and incorrect ergonomics at home or work.
Some common types of poor posture are:
- Forward head posture
- Kyphosis posture
- Flat back posture
- Swayback posture
Types of Posture
Posture is how you hold your body. There are 3 types where you can check your spine health.
- Neutral posture implies that the Back is straight up and down (vertical), and not leaning forward or back at the waist. The upper back and lower lumbar curve are supported by the chair’s back or backrest. Neck. The neck is relaxed.
- Static posture is how you hold yourself when you are not moving, like when you are sitting, standing, or sleeping.
- Dynamic posture is how you hold yourself when you are moving, like when you are walking, running, or bending over to pick up something.
Neutral
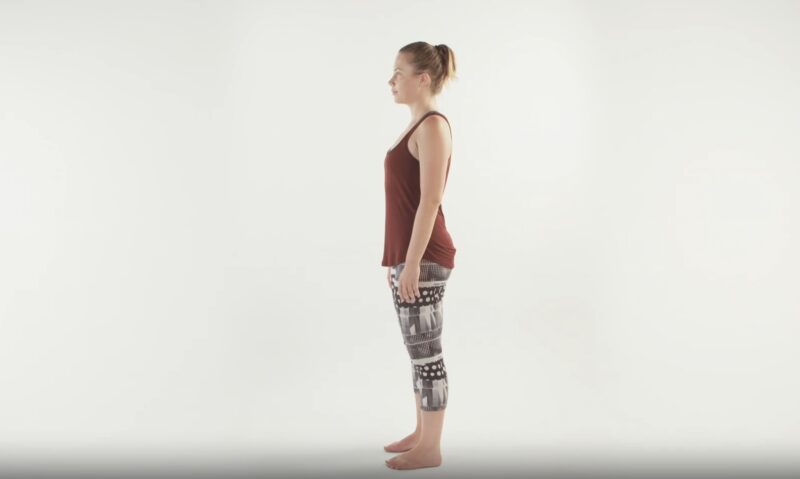

Neutral posture, also known as good posture, refers to the ideal alignment of the spine, head, shoulders, and hips. This alignment helps evenly distribute the body’s weight and minimizes stress on the muscles, ligaments, and bones. Neutral posture ensures optimal balance, movement efficiency, and reduced risk of injury.
Here’s a quick checklist for achieving a neutral posture:
- Keep your head straight and in line with the shoulders
- Align the ears with the shoulders
- Gently engage the core muscles
- Maintain a natural curve in the lower back
- Roll your shoulders back and down, avoiding hunching
- Keep your feet hip-width apart with equal weight distribution
Dynamic
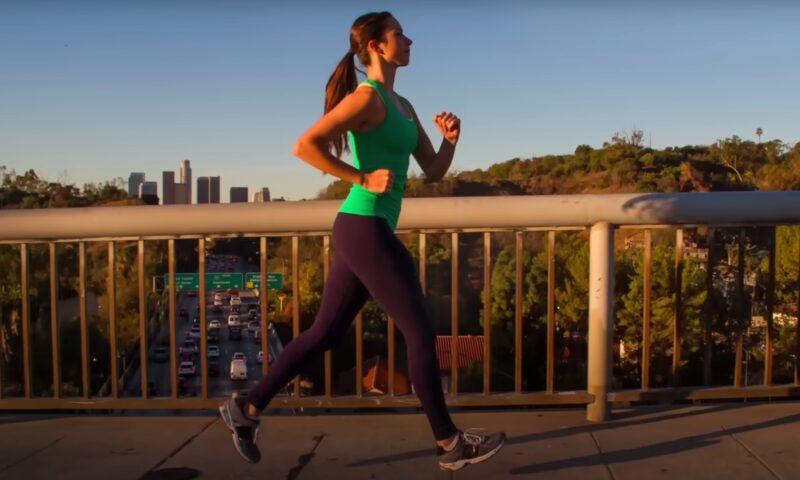 Dynamic posture refers to the way your body is positioned when in motion, such as walking, running, or performing physical activities. Maintaining proper alignment and utilizing the correct muscle groups during movement is essential for overall muscular health and injury prevention. Some tips for maintaining dynamic posture are:
Dynamic posture refers to the way your body is positioned when in motion, such as walking, running, or performing physical activities. Maintaining proper alignment and utilizing the correct muscle groups during movement is essential for overall muscular health and injury prevention. Some tips for maintaining dynamic posture are:
- Avoid locking your knees when walking
- Keep the chest up, shoulders back and down
- Engage the core muscles during activities
- Be mindful of foot placement and stride length
- Choose supportive footwear for different activities
Static Posture
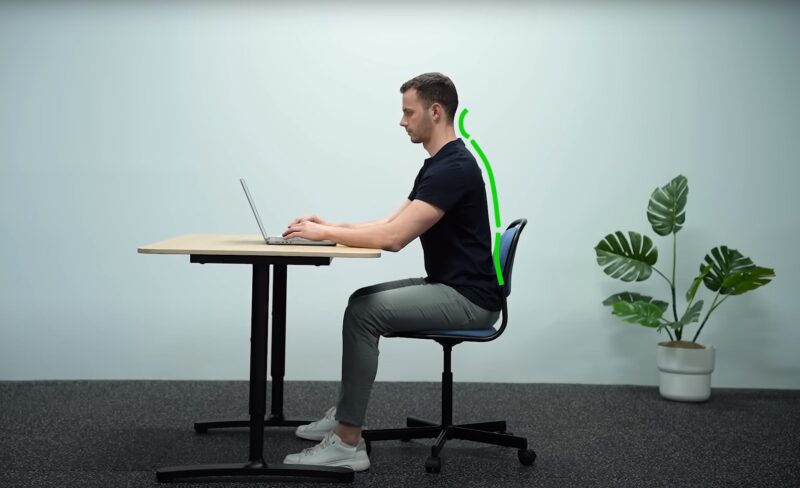 Contrastingly, static posture refers to the position of the body when at rest, such as when sitting, standing, or lying down. Just like dynamic posture, maintaining proper spinal alignment in static positions is crucial for musculoskeletal health, as well as preventing pain and discomfort.
Contrastingly, static posture refers to the position of the body when at rest, such as when sitting, standing, or lying down. Just like dynamic posture, maintaining proper spinal alignment in static positions is crucial for musculoskeletal health, as well as preventing pain and discomfort.
Here are a few guidelines for improving static posture:
Sitting:
- Sit back in a chair with lumbar support for the lower back
- Adjust the chair height to keep feet flat on the ground
- Keep the elbows close to the body while typing or using a mouse
- Take breaks every 30 minutes to stand and stretch
Standing:
- Stand tall, keeping the shoulders back and down
- Soften the knees to avoid locking them
- Engage the core muscles for added support
- Wear comfortable shoes with adequate support
By incorporating these practices, individuals can improve their posture in both dynamic and static positions, leading to enhanced musculoskeletal health, better balance, and decreased risk of injury.
Common Postural Problems
Kyphosis
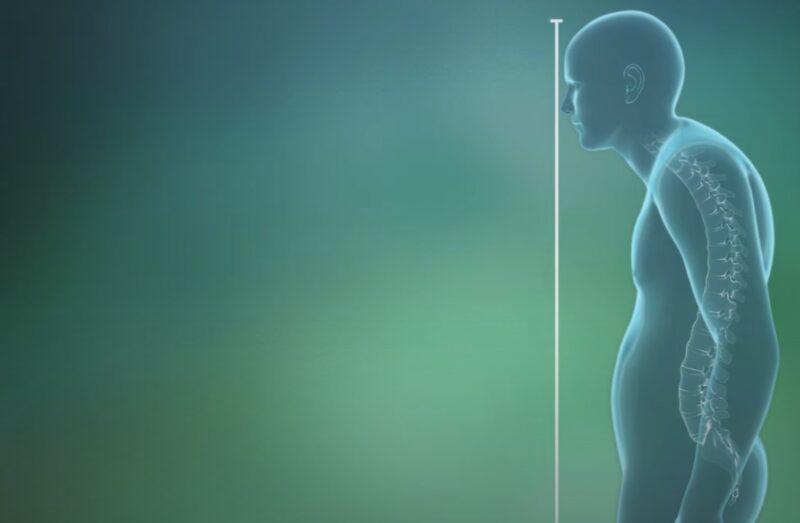

Kyphosis is characterized by an exaggerated curve in the upper back, often leading to a hunched or rounded-shoulder appearance. This postural problem may result from poor sitting habits, muscle imbalances, or genetic factors.
Kyphosis can cause discomfort and is associated with various health issues such as breathing difficulty and reduced mobility. To alleviate kyphosis, individuals can practice posture-correcting exercises and focus on strengthening their back muscles.
Lordosis
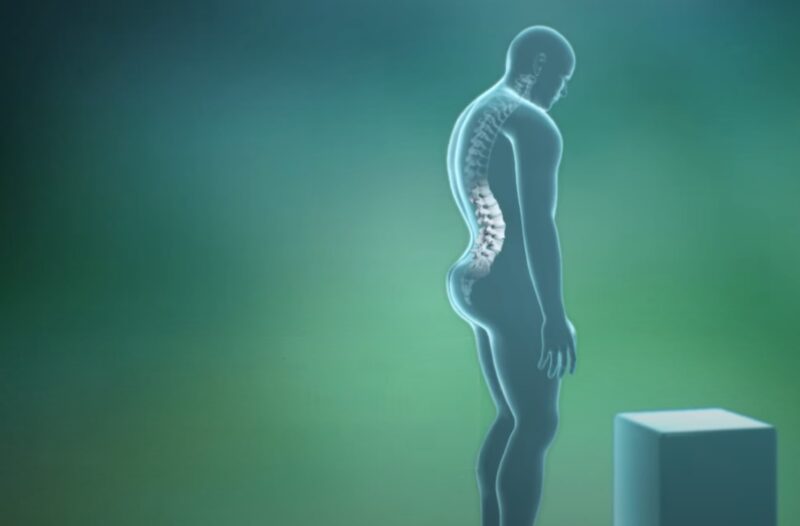
Unlike kyphosis, lordosis involves an excessive inward curve of the lower back. This postural issue often causes the abdomen and buttocks to protrude, creating an exaggerated arch in the spine.
Lordosis may be caused by factors such as muscle imbalances, tight hip flexors, or weak core muscles. Addressing lordosis typically involves engaging in core-strengthening exercises and stretching tight muscles to achieve a more balanced alignment.
Scoliosis
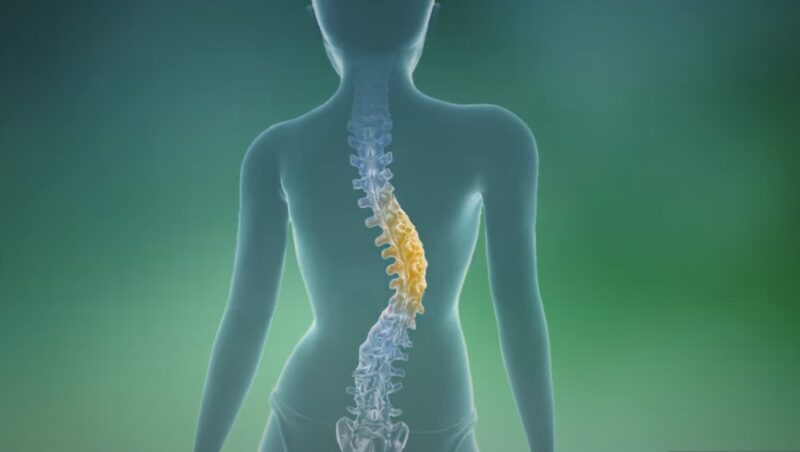
Scoliosis is a spinal condition characterized by a sideways curvature of the spine, usually in an “S” or “C” shape. It can range from mild to severe, with some individuals experiencing pain, discomfort, and limitations in physical activities.
The severity and progression of scoliosis often determine the course of treatment or intervention. Bracing, physical therapy, and surgery for more severe cases are some of the management options available for those diagnosed with scoliosis.
Anterior Pelvic Tilt
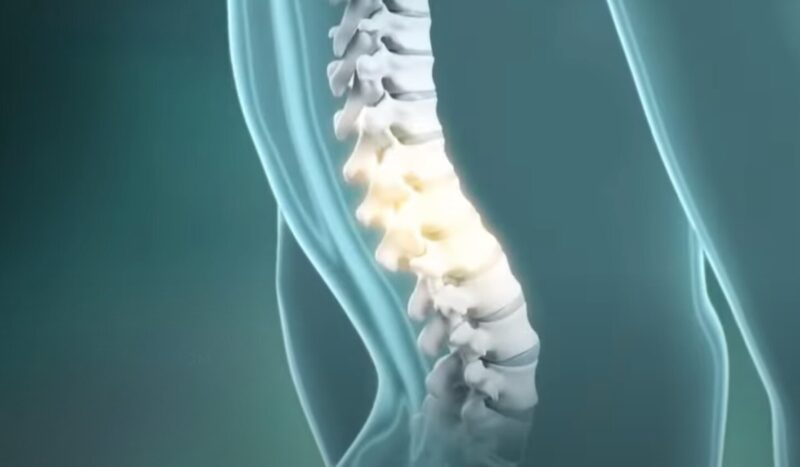
An anterior pelvic tilt refers to the forward tilting of the pelvis, resulting in a misalignment of the spine and lower back. This condition is often caused by prolonged sitting, muscle imbalances, or weak core muscles.
Some common consequences of anterior pelvic tilt include lower back pain and decreased hip mobility. Addressing this postural issue often involves strengthening the core muscles and glutes, as well as stretching tight hip flexors to achieve a more neutral pelvic position.
Impact on Health
Musculoskeletal Pain
Poor posture can lead to various forms of musculoskeletal pain, including back pain, neck pain, and shoulder strain. Misalignments in the spine can create imbalances, putting extra stress on certain muscles and joints, ultimately leading to discomfort and pain.
For example, when you slouch, your head moves forward, which can cause strain on the neck and shoulders. According to Cleveland Clinic, consistently ignoring advice on good posture can set you up for long-term joint damage.
Respiratory Issues
Believe it or not, an incorrect posture can also have an impact on your respiratory system. Slouching or hunching over can compress the diaphragm and chest cavity, making it difficult for the lungs to fully expand and limiting overall airflow.
Consequently, shallow breathing may lead to lower oxygen levels in your blood, potentially aggravating existing respiratory problems. U.S. News mentions that bad posture can contribute to respiratory issues.
Digestive Problems
Your gastrointestinal system may also suffer if you maintain poor posture. When your body is not properly aligned, it can compress your organs, affecting the functioning of your digestive tract.
Symptoms such as acid reflux, bloating, and constipation can result from consistently poor posture, as mentioned by Lifespan. Correcting posture can help alleviate these issues and promote optimal digestive function.
In summary, maintaining good posture is essential for preventing not only musculoskeletal pain, but also respiratory and digestive problems.
Improving posture for health – Prevention is The Key
Ergonomics at Work
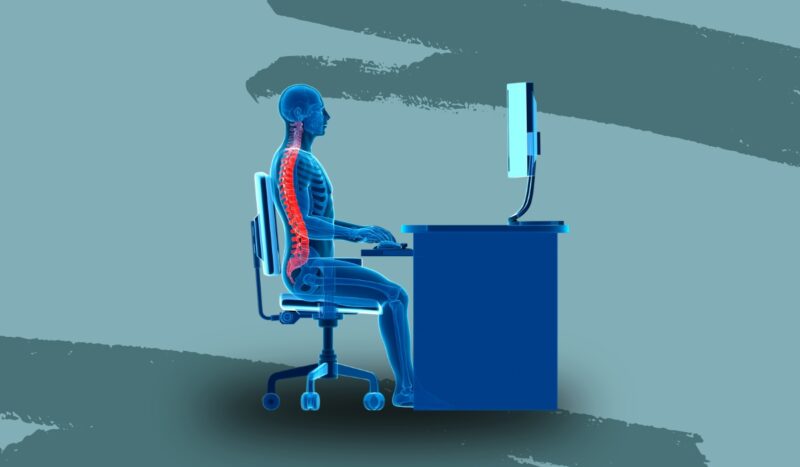 A key factor in maintaining good posture is ergonomics at the workplace. Proper ergonomic arrangements consist of:
A key factor in maintaining good posture is ergonomics at the workplace. Proper ergonomic arrangements consist of:
- Adjusting your computer monitor to eye level
- Utilizing a chair with lower back support
- Keeping your knees and elbows at a 90-degree angle
- Ensuring your feet rest flat on the floor or a footrest
By following these suggestions, you can reduce strain and promote a healthier posture.
Exercise and Stretching
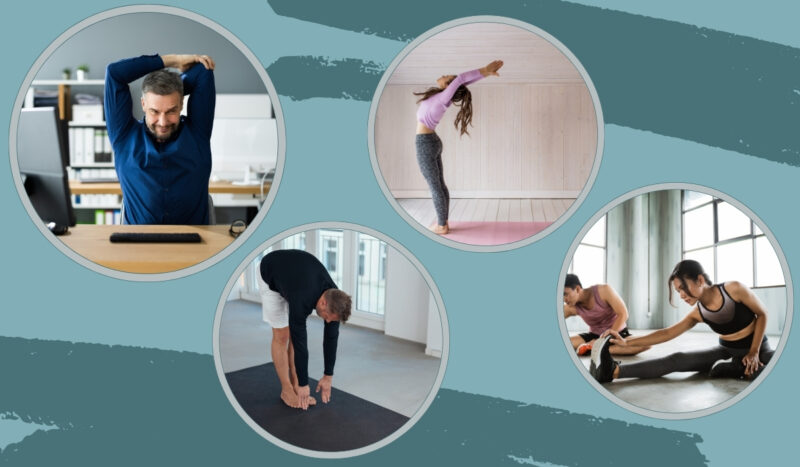 Incorporating regular exercise and stretching routines is essential for keeping your body strong, flexible, and capable of maintaining good posture. Some useful exercises include:
Incorporating regular exercise and stretching routines is essential for keeping your body strong, flexible, and capable of maintaining good posture. Some useful exercises include:
- Core strengthening: Planks, bridges, and abdominal exercises can help improve core stability.
- Chest flexibility: Doorway stretches and pectoral muscle stretches can enhance chest flexibility and posture.
- Upper back strength: Rows and reverse fly exercises target the upper back muscles, which support correct posture.
Implementing these exercises into your daily routine will contribute to better posture by strengthening the necessary muscles and increasing flexibility.
Posture Training Tools
Various posture training tools are available to assist in correcting and maintaining proper alignment. Some popular options include:
- Lumbar rolls: These cylindrical supports can be placed behind the lower back when sitting to encourage proper spinal alignment.
- Posture shirts: Designed with built-in tension bands, these shirts gently pull the shoulders back, promoting better posture.
- Posture apps: Smartphone applications can be used to track and remind users to maintain proper posture throughout the day.
Incorporating these posture training tools can be a valuable addition to your posture improvement efforts. However, it’s essential to consult with a professional before trying any tools, as they may not be suitable for everyone.
FAQ
Conclusion
Improving posture for health by taking small steps each day will make you happier. Be kind to your body by stretching, using good posture habits at work and home, and strengthening exercises. Don’t worry if it’s not perfect right away.
With practice, better posture will become a healthy habit. Remember to stand tall, keep your shoulders back, and take breaks to move. Soon you’ll feel the benefits of a straighter spine and renewed energy. Your best life starts with how you carry yourself, so focus on posture for a healthier you!

