Living with spinal stenosis pain can feel like a constant battle that intrudes on the simplest of your day-to-day tasks.
As you navigate the challenges posed by this condition, finding effective pain relief is paramount.
Pain management, often through the use of medications, is a crucial aspect of treatment strategies, which can include a combination of therapies tailored to reduce discomfort and improve mobility.
Key Takeaways
Discomfort
Spinal stenosis leads to discomfort because it causes a reduction in the space within your spinal canal, leading to nerve pressure. When your spinal nerves are squeezed, you may experience pain, muscle cramping, weakness, and tingling sensations. This pain can extend from your back down to your legs.
Certain activities exacerbate this pain, such as:
- Walking for extended periods
- Jumping
- Bending or twisting your spine excessively
- Participating in contact sports (e.g., football)
- Lifting objects with a bend in your back
Strategies to Halt the Progression of Spinal Stenosis
- Limit Straining Movements: Steer clear of activities that overburden your spine.
- Initiate Low-Impact Exercise: Engage in activities like walking or swimming to preserve flexibility and strength without stressing your spine.
- Focus on Posture: Cultivate an ergonomic stance to reduce pressure on spinal components.
- Avoid Nicotine: Abstain from smoking to ensure adequate spinal blood flow.
- Manage Body Weight: Aim to keep a normal weight to decrease spinal load.
- Regular Stretching: Incorporate stretching exercises to mitigate muscle tightness and discomfort.
Therapeutic Exercises and Strategies
Therapeutic training is a non-invasive approach to reduce severe spinal stenosis discomfort. It emphasizes improving spinal alignment and nerve decompression through exercise, stretches, and supportive measures. Benefits include:
- Lessened discomfort and rigidity around the back.
- Alleviation from nerve impingement.
- Core muscle support.
- Enhanced alignment in the lower spine.
Practices may incorporate heat or cold applications and electrical nerve stimulation to support healing and pain relief.
Medications for Lower Back Discomfort
To manage intense discomfort due to spinal stenosis, several medications are utilized:
- NSAIDs: These drugs, including over-the-counter options like ibuprofen and naproxen, as well as prescription forms, target pain and swelling.
- Antidepressant Medication: These can modify neurotransmitter levels, which may reduce pain sensation, though it may take time before they become effective.
- Medicines Targeting Nerve Pain: Drugs such as gabapentin and pregabalin focus on nerve-related pain.
- Epidural Steroid Injections: Delivering corticosteroids directly into the affected area can reduce inflammation but are limited in frequency due to potential tissue damage with overuse.
- Muscle Relaxants: These can relieve symptoms like muscle spasms, numbness, and radiating pain in spinal stenosis cases.
Optimal Muscle Relaxants
When managing spinal stenosis, selecting an effective muscle relaxant tailored to your needs is critical. Among the recommended options are baclofen, cyclobenzaprine, and methocarbamol.
Baclofen
This muscle relaxer addresses muscle spasms associated with spinal disorders. It aids in reducing pain, enhancing muscle movement, and lessening stiffness.
Common side effects:
- Tiredness
- Feeling weak
- Unsteadiness
- Sleep disturbances
- Nausea
- Increased urination
- Headaches
- Constipation
Cyclobenzaprine

Acting within the brain to calm muscle overactivity, cyclobenzaprine is useful for short-term relief in spinal stenosis-related pain and functional improvement.
Common side effects:
- Clumsiness
- Dry mouth
- Confusion
- Fainting
- Constipation
- Drowsiness
- Nausea
- Heartburn
Methocarbamol
Methocarbamol provides comfort from pain and muscle spasms by intercepting pain signals to the brain. It is perceived to have milder sedative effects and a decreased potential for abuse.
Common side effects:
- Drowsiness
- Dizziness
- Upset stomach
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Lightheadedness
- Headaches
- Blurred vision
Your medical provider will guide you in choosing the most suitable option based on your individual situation. It’s essential to weigh the benefits against the possible side effects.
Effective Management of Spinal Pain with Medications

Combining Chlorzoxazone with Ibuprofen for Lower Back Pain
Research indicates that pairing chlorzoxazone, a prescription muscle relaxant, with ibuprofen, a widely accessible anti-inflammatory drug, can offer enhanced relief for acute lower back pain compared to ibuprofen alone. Chlorzoxazone targets muscle tension and pain, while ibuprofen focuses on reducing inflammation.
Carisoprodol and Aspirin: A Synergistic Duo for Spinal Soreness
For pain stemming from spinal stenosis, the mix of carisoprodol, a doctor-prescribed muscle relaxant, with aspirin, an inflammatory reducer, is another traditional approach. Carisoprodol helps soothe strained muscles, whereas aspirin manages pain and swelling.
Availability of Combined Muscle Relaxants and NSAIDs
You will not find over-the-counter pills that merge muscle relaxants and NSAIDs in the United States. However, adjacent to us in Canada, Robax Platinum is an available treatment option incorporating both ibuprofen and methocarbamol to ease pain and muscle rigidity.
Precautions When Using Muscle Relaxants with Pain Meds
When considering medications for back discomfort related to spinal stenosis, combining muscle relaxants and pain relievers requires careful consideration. It’s crucial to avoid mixing muscle relaxants with opioid analgesics due to the risk of severe side effects like respiratory distress. Always consult your physician, and remember that muscle relaxants are typically not for prolonged use.
| Medication Type | Purpose | Combination Use |
|---|---|---|
| Chlorzoxazone | Muscle spasms and pain relief | With Ibuprofen |
| Carisoprodol | Muscle tension relief | With Aspirin |
| NSAIDs | Inflammation and pain reduction | Over-the-counter |
| Methocarbamol | Alleviate muscle rigidity | With Ibuprofen (CA) |
| Opioid Analgesics | Pain relief (Caution advised) | Not recommended |
Note: Always seek medical advice before beginning any new medication regimen, especially when combining drugs to treat pain and muscle spasms.
Optimal Therapy for L4-L5 Spinal Stenosis
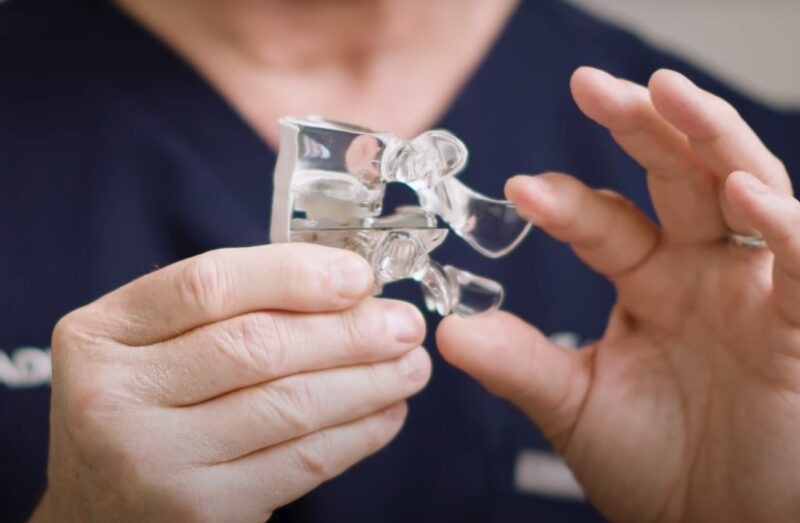

When non-surgical approaches fail, consider spinal decompression with the TOPS System for effective relief.
Embrace a New Chapter in Spinal Health
Regain the comfort and flexibility you’ve been missing with advanced treatments for spinal stenosis. Incorporating the latest surgical advancements, innovative options like the TOPS System offer a promising future without the constraints of traditional spinal fusion.
Redefining Spinal Treatment:
- Spinal Decompression: Relieves nerve pressure by removing bone or tissue, with procedures like laminectomy.
- Avoiding Fusion Drawbacks: Traditional fusion reduces mobility and might cause adjacent segment degeneration.
- TOPS System Advantage: The FDA-approved TOPS System offers flexibility post-decompression, without the downsides of fusion.
Who Can Benefit:
- Individuals aged 35 to 80
- Patients with degenerative spondylolisthesis
- Those experiencing moderate to severe lumbar spinal stenosis
Why Consider TOPS?
- Maintains mobility and allows bending and twisting
- Minimized postoperative pain
- Endorsed by the FDA as superior to fusion for specific spinal conditions
If persistent spinal stenosis symptoms withstand non-invasive methods, consult a specialist to explore these life-changing surgical innovations. Your journey to reclaiming a pain-free and active lifestyle can begin now.
FAQ
Exercises to Steer Clear of When You Have Spinal Stenosis?
If you’re dealing with spinal stenosis, certain exercises might worsen your condition. To prevent discomfort and potential injury:
- Avoid high-impact activities like running or jumping.
- Steer clear of weightlifting that strains the back, such as deadlifts or overhead presses.
- Minimize activities that involve extreme spinal flexion or extension, like touching your toes or doing backbends.
What Are Effective Ways to Handle Nerve Compression in the Lower Spine?
For nerve compression at the L4 and L5 vertebrae, treatment options can include:
- Physical therapy to strengthen supporting muscles and minimize pain.
- Medications, such as over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription drugs for more severe pain.
- Epidural steroid injections to reduce inflammation around the affected nerves.
Cutting-Edge Treatments for Spinal Stenosis?
Recent advancements in treating spinal stenosis involve:
- Minimally invasive surgery techniques that reduce recovery times.
- Neuromodulation, such as spinal cord stimulation.
- Innovative physiotherapy approaches, including aquatic therapy.
Most Successful Spinal Stenosis Interventions?
The treatments with the highest success rates often involve a combination of:
- Conservative measures, including physical therapy and anti-inflammatory medications.
- Interventional procedures like epidural steroid injections, when appropriate.
- Surgical intervention, considered as a last resort when other treatments are ineffective.
Management of Spinal Stenosis in the Elderly?
In elderly patients, spinal stenosis should be managed with a focus on:
- Maximizing non-invasive treatments such as physical therapy and medication.
- Monitoring and balancing rest with activity to prevent stiffness.
- Evaluating the risks and benefits of surgery, given the patient’s overall health.
Typical Walking Impediments for Spinal Stenosis Sufferers?
Those with spinal stenosis often face challenges when walking, such as:
- Neurogenic claudication: leg pain and weakness that improves with rest.
- Reduced endurance: difficulty walking long distances.
- Balance issues: increased risk of falls due to numbness in the legs.
Conclusion
Living with spinal stenosis requires a comprehensive and informed approach to manage pain and maintain quality of life.
Effective management includes a combination of medication, therapeutic exercises, and when necessary, advanced surgical options like the TOPS System.
Understanding the condition, avoiding aggravating activities, and exploring both traditional and innovative treatments can help individuals navigate the challenges of spinal stenosis with greater ease and comfort.